

APS Floc Logs® can be used to clarify stormwater removing turbidity such as sediment, heavy metals, and inanimate nutrients reducing the total suspended solids.
Water treatment is much easier when the soil is treated at the source. Less sediment being picked up by stormwater means the less sediment that is moving off site, the less turbid your stormwater is, and ultimately the more cost effective solution.
Polymer Enhanced Stormwater Treatment Ditches are used to introduce site-specific anionic polymers to turbid waters in such a manner to facilitate mixing and reaction between the polymer and the suspended particles. The Floc Logs® are designed for use in flowing conditions and can be used with passive flow or active pumping systems. Mixing and reaction time with the Floc Logs® are extremely important to ensure the suspended sediment is fully flocculated.
Collection of the flocculated particulate that forms will greatly reduce the turbidity of the stormwater. The particulate formed can be captured by filtering through silt fence, mulch, straw, settling in a sediment pond, or flowing over jute fabric after the mixing reaction has been completed to increase final water clarity.
Overview of a Polymer Enhanced Water Treatment System:
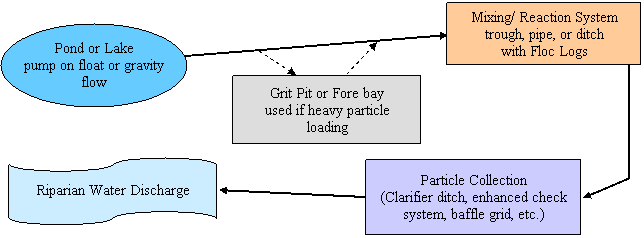
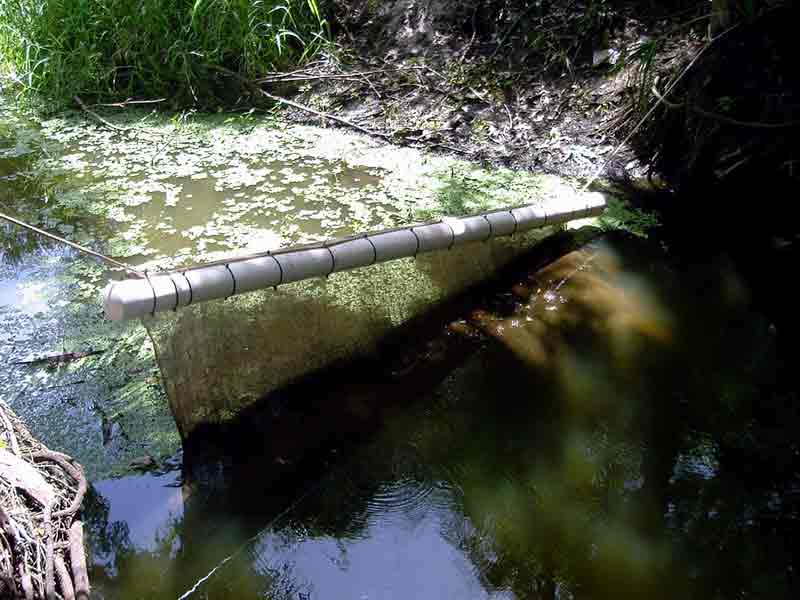
Primary Sediment Pond / Grit Pit:
A primary sediment pond or grit pit may be required to reduce the sediment load before treatment. These are placed "upstream" of the mixing system to prevent sediment from burying the mixing system with excess sediment loads. It allows the heaviest sediment to settle out prior to treatment with the polymer. If sediment loads of the turbid water exceed 40,000 NTU or 4% solids, such as in active dredging operations, we suggest including a primary sediment pond or grit pit.
Mixing / Reaction Systems
To introduce site-specific Floc Logs® to turbid waters in such a manner to facilitate mixing and reaction between the anionic polymer and the suspended particles.
Open ditch design:
A ditch is created, either by digging out the bed or building up the walls. The site-specific Floc Logs® are secured along the ditch, allowing the water to flow over and around them. Checks can be placed along the ditchline to increase turbulence and mixing with the Floc Logs®.
Split-pipe design:
Water flows down the split pipe, lined with jute to help collect the reacted sediment. In the photo on the right, you can see where the water is flowing out of the large red fractionation tank which was acting like a sediment pond to collect the heaviest sediment and prevent the Floc Logs® from being buried in sediment.
Tank Systems with Split Pipe Launder
The Water Clarification Treatment Split Pipe Launder System is designed to perform in a variety of flow conditions. The launder needs to be long enough to meet the required reaction time as seen on the site-specific lab report. Increasing the length of the launder will result in better mixing and reaction forming more flocculated particulate.
Filling the launder with sediment will reduce/ impair the reaction. The launder needs to be installed with a gradient drop that allows the turbid water to flow through it; higher sediment load will require a greater angle to allow the Floc Logs to mix effectively.
Sediment Collection Devices
Used to capture and filter out the reacted sediment, to discharge clarified water.
Dispersion Fields:
Allow the treated water to spread out over a delta to slow it''''s velocity and allow reacted sediment to drop out of suspension. The photos below show a series of checks built out of sandbags laid across the delta to slow the velocity in a smaller area. Lining the dispersion field with jute matting will provide surface area for the particulate to adhere to, using APS Silt Stop® on the jute matting will enhance it''''s "stickiness" thereby increasing it''''s sediment collection capability.
Baffle Grids:
Baffle panels are constructed of layers of geotextile fabric attached to a wooden frame. Series of these frames are placed upright, perpendicular to the flow of water. The water, after being treated with the Floc Logs®, passes through the baffle grid, where the treated sediment in captured by the fabric, allowing the clarified water to pass through.

Waddles or Check Systems:
The photos below are of waddle or check systems, lined with jute fabric. The jute fabric provides surface area for the flocculated sediment to adhere to (as shown in the photo on the left). The treatment ditch on the right shows the waddles, which slow the velocity of the water and allow time for the sediment to drop out of suspension and collect on the jute fabric.

Particle Curtains:
Particle curtains are used when working in a flowing stream. They are constructed using open-weave geotextile fabrics attached to floats which are hung in the water. When placed in rows one after another, they are similar to a baffle grid, collecting reacted sediment as the water passes through the curtains.

